详解全局事务注解@GlobalTransactional的识别
温馨提示:这篇文章已超过489天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
这篇文章主要为大家介绍了详解全局事务注解@GlobalTransactional的识别源码解析,有需要的朋友可以借鉴参考下,希望能够有所帮助!
一、声明式全局事务
在Seata示例工程中,能看到@GlobalTransactional,如下方法示例:
@GlobalTransactional
public boolean purchase(long accountId, long stockId, long quantity) {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
LOGGER.info("New Transaction Begins: " + xid);
boolean stockResult = reduceAccount(accountId,stockId, quantity);
if (!stockResult) {
throw new RuntimeException("账号服务调用失败,事务回滚!");
}
Long orderId = createOrder(accountId, stockId, quantity);
if (orderId == null || orderId <= 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("订单服务调用失败,事务回滚!");
}
return true;
}purchase方法上加上此注解,即表示此方法内的reduceAccount和createOrder两个微服务调用也将加入到分布式事务中,即扣除账户余额与创建订单将具有分布式事务的数据一致性保障能力。
了解 Spring 注解事务实现的话,应该也能推测出,Seata 的事务能力也可能是基于 Spring 的 AOP 机制,给标注了@GlobalTransactional 的方法做 AOP 增加,织入额外的逻辑以完成分布式事务的能力,伪代码大致如下:
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrentOrCreate();
try {
tx.begin(xxx);
...
purchase(xxx)//给purchase增加全局事务处理能力
...
tx.commit();
} catch (Exception exx) {
tx.rollback();
throw exx;
}二、@GlobalTransactional 注解如何被识别?
2.1 运行环境
1)引入seata-spring-boot-starter模块
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${seata.version}</version>
</dependency>在spring.factories 中有自动装配类SeataAutoConfiguration
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ ... io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure.SeataAutoConfiguration ...
此类负责处理全局事务扫描及设置,其中就有@GlobalTransactional。
2)条件要求:
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = SEATA_PREFIX, name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@AutoConfigureAfter({SeataCoreAutoConfiguration.class})
public class SeataAutoConfiguration从类的自动装备条件,可看出要满足 2 个条件:
@ConditionalOnProperty,表明若要生效须具备以下配置条件:
seata.enabled = true
@AutoConfigureAfter,表示从 bean 的加载顺序来看,要求是在SeataCoreAutoConfiguration之后,SeataCoreAutoConfiguration又是什么呢?
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = SEATA_PREFIX, name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure.properties")
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class SeataCoreAutoConfiguration {
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_PROVIDER)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = {BEAN_NAME_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_PROVIDER})
public SpringApplicationContextProvider springApplicationContextProvider() {
return new SpringApplicationContextProvider();
}
}从源码可知,也很清晰,大概有几个功能点:
同样要求
seata.enabled = true另外会扫描"io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure.properties"
会提供一个
SpringApplicationContextProvider,基于 Spring 的程序中,很常见这种方式,用于提供ApplicationContext,通常用于方便获取 bean 和添加 bean 等。
public class SpringApplicationContextProvider implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.setProperty("file.listener.enabled", "false");
ObjectHolder.INSTANCE.setObject(OBJECT_KEY_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT, applicationContext);
}
}2.2 功能-注入事务执行失败处理器FailureHandler
注入一个FailureHandler,其默认实现DefaultFailureHandlerImpl中只会打印错误日志,建议重写,异常发生时及时告知使用者。
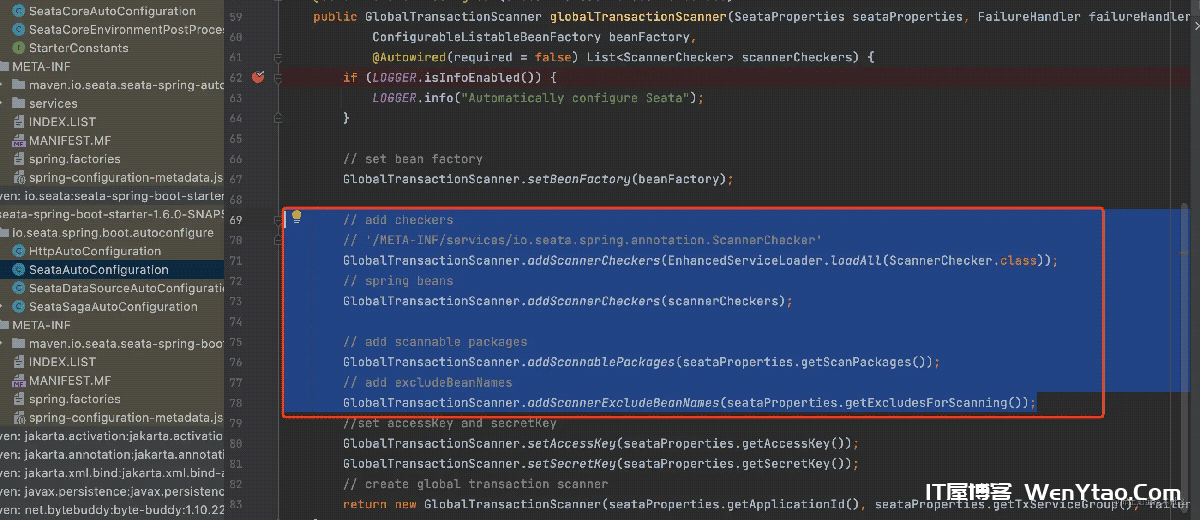
2.3 功能-构建全局事务扫描器GlobalTransactionScanner
构建全局事务扫描器GlobalTransactionScanner,注入到容器中,其内部做 2 件事情
会初始化
TM、RM客户端扫描
Bean,对添加了全局事务注解的类(@GlobalTransactional、@GlobalLock、@TwoPhaseBusinessAction)生成代理对象,做AOP增强,添加对应的拦截器(拦截器内补充分布式事务的能力)
public class GlobalTransactionScanner extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator
Spring 中 Bean 的关键初始化过程:
实例化 -> 属性注入 -> postProcessBeforeInitialization -> afterPropertiesSet/init 方法 -> postProcessAfterInitialization
从以下堆栈可以看出,AbstractAutoProxyCreator在 bean 初始化完成之后创建它的代理 AOP 代理,通过wrapIfNecessary判断是否该 bean 是否存在全局事务注解,如果有则需要增强,添加相应的拦截器。
wrapIfNecessary:269, GlobalTransactionScanner (io.seata.spring.annotation) postProcessAfterInitialization:293, AbstractAutoProxyCreator (org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy) applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization:455, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support) initializeBean:1808, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support) doCreateBean:620, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
先看一个关键方法existsAnnotation,当扫描到 bean 之后,获取 bean 的原始类型,然后通过此方法原始类型的类或者方法中是否有@GlobalTransactional或@GlobalLock注解
private boolean existsAnnotation(Class<?>[] classes) {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(classes)) {
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
if (clazz == null) {
continue;
}
//判断类上是否有注解@GlobalTransactional
GlobalTransactional trxAnno = clazz.getAnnotation(GlobalTransactional.class);
if (trxAnno != null) {
return true;
}
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//判断方法上是否有注解@GlobalTransactional
trxAnno = method.getAnnotation(GlobalTransactional.class);
if (trxAnno != null) {
return true;
}
//判断方法上是否有注解@GlobalLock
GlobalLock lockAnno = method.getAnnotation(GlobalLock.class);
if (lockAnno != null) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}wrapIfNecessary方法中实现了事务注解识别的核心逻辑:
/**
* The following will be scanned, and added corresponding interceptor:
*
* TM:
* @see io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactional // TM annotation
* Corresponding interceptor:
* @see io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionalInterceptor#handleGlobalTransaction(MethodInvocation, AspectTransactional) // TM handler
*
* GlobalLock:
* @see io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalLock // GlobalLock annotation
* Corresponding interceptor:
* @see io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionalInterceptor#handleGlobalLock(MethodInvocation, GlobalLock) // GlobalLock handler
*
* TCC mode:
* @see io.seata.rm.tcc.api.LocalTCC // TCC annotation on interface
* @see io.seata.rm.tcc.api.TwoPhaseBusinessAction // TCC annotation on try method
* @see io.seata.rm.tcc.remoting.RemotingParser // Remote TCC service parser
* Corresponding interceptor:
* @see io.seata.spring.tcc.TccActionInterceptor // the interceptor of TCC mode
*/
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// do checkers
// seata提供的有扩展逻辑用于辅助判断是否需要增强
if (!doCheckers(bean, beanName)) {
return bean;
}
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
//如果已被代理,则跳过该Bean ,PROXYED_SET是一个Set<String> 集合
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
//check TCC proxy
//判断是否TCC模式,如果是TCC,则添加TCC 拦截器
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
// init tcc fence clean task if enable useTccFence
TCCBeanParserUtils.initTccFenceCleanTask(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName), applicationContext);
//TCC interceptor, proxy bean of sofa:reference/dubbo:reference, and LocalTCC
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)interceptor);
} else {
//非TCC模式
// 查询Bean的 Class 类型
Class<?> serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class<?>[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
//判断是否有GlobalTransactional或者GlobalLock注解,如果没有就不会代理,直接返回bean
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
// 初始化GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
//添加 禁用全局事务的监听器
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
LOGGER.info("Bean[{}] with name [{}] would use interceptor [{}]", bean.getClass().getName(), beanName, interceptor.getClass().getName());
// 判断是否已经是AOP代理类,如果不是,则执行父类的wrapIfNecessary
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
// 给代理对象添加拦截器
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
int pos;
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
// Find the position based on the advisor's order, and add to advisors by pos
pos = findAddSeataAdvisorPosition(advised, avr);
advised.addAdvisor(pos, avr);
}
}
//标识该bean已经代理过,本方法入口处有判断
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}Seata 提供的有扩展逻辑用于辅助判断是否需要增强,这里的扩展点有好几个,这些扩展是用于安全保障,使用者可以按需采用。
三、小结:
本篇梳理了引入seata-spring-boot-starter模块后,其内部会通过的自动装配机制会在SeataAutoConfiguration类中,扫描具有@GlobalTransactional全局事务注解的类和方法的 bean,并对这类 bean 添加GlobalTransactionalInterceptor,进行 AOP 增强,加入分布式事务的能力,增强后的功能复杂