Java Collection接口中的常用方法总结
温馨提示:这篇文章已超过513天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
本节将大概用代码案例简单总结一下 Collection 接口中的一些方法,我们会以他的实现类 Arraylist 为例创建对象。一起来看看吧!
Collection 接口中的常用方法
添加
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @Author:Aniu
* @Date:2022/12/4 16:19
* @description TODO
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
// add(Object e) 增加
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
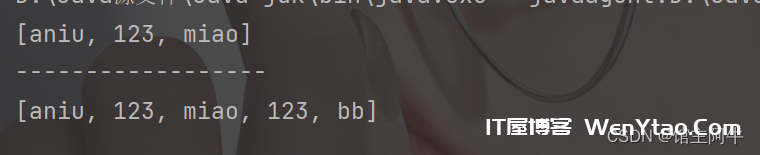
System.out.println(coll);
System.out.println("------------------");
// addAll() 将另一个集合中的元素添加到当前集合中
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(123);
coll1.add("bb");
coll.addAll(coll1);
System.out.println(coll);
}
}求长度
// size() 求添加的元素个数
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
System.out.println(coll.size());判断当前集合是否为空
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
//isEmpty() 判断当前集合是否为空
System.out.println(coll.isEmpty());清空集合元素
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
//clear() 清空集合元素
System.out.println(coll.clear());判断当前对象是否在集合中
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
// contains() 判断对象是否在当前集合中
System.out.println(coll.contains(new String("aniu")));这里要注意的是,contains本质上是用equals比较的,因此,对于自定义对象,要记得重写equals方法!
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(123);
coll1.add("aniu");
// containsAll() 判断形参集合中的元素是否在当前集合中
System.out.println(coll.containsAll(coll1));本质上依旧是用equals一个个比较
移除
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new String("miao"));
// remove() 移除
coll.remove(123);
System.out.println(coll);
System.out.println("------------");
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(456);
coll1.add(new String("miao"));
// removeAll() 从当前集合中移除形参集合中的所有元素,即差集
coll.removeAll(coll1);
System.out.println(coll);removeAll() 相当于求差集,那么也有对应求交集的!
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
coll.add(new String("miao"));
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(123);
coll1.add(new String("miao"));
// retainAll() 即求交集
coll.retainAll(coll1);
System.out.println(coll);判断相等
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(123);
coll.add("aniu");
// equals() 判断两个集合是否相等,因为这里使用ArrayList()实现,因此要考虑顺序
System.out.println(coll.equals(coll1));集合转换为数组
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("aniu");
coll.add(123); //自动装箱
// toArray() 集合转数组
Object[] arr = coll.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));数组转换为集合
既然说到了集合转数组,这里就说一下数组转集合!
List list = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"aniu", "tom"});
System.out.println(list);结语
本来关于这些api是不想总结的,像String中的一些api,和其他语言中的差不多,我就没总结!集合中的方法名与其他语言稍微有不同,这里快速过一下。